Business process reengineering is one of the application areas of BPM, which aims to recreate or redesign business processes to optimize cost and improve efficiency.
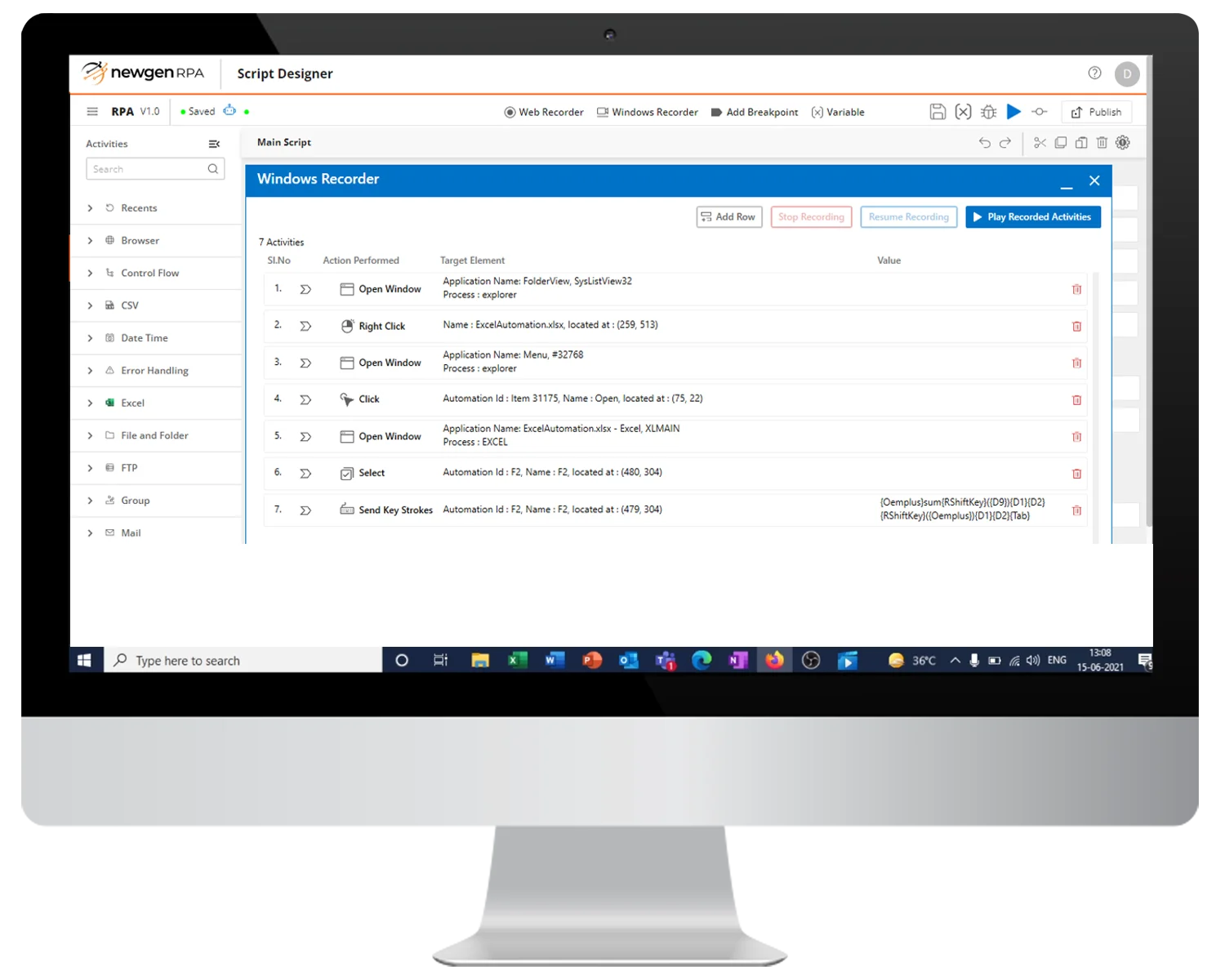
Automate for outcomes with the most comprehensive process automation platform. Leverage the power of workflow automation unified with content services, business rules, omnichannel communication, case management, RPA, and AI to deliver efficient, intelligent, and context-aware processes. Go beyond automation to build a continuously improving agile organization at a scale of thousands of processes. Modernize work to unleash automated and touchless self-service that makes not only the customer happy, but also employees and partners.
With our Intelligent Process Automation Platform, You Can Do it All!
Newgen Software’s roots are at the intersection of sophisticated content management, case management, and process management.
The Forrester Wave™: Digital Process Automation Software, Q4 2021

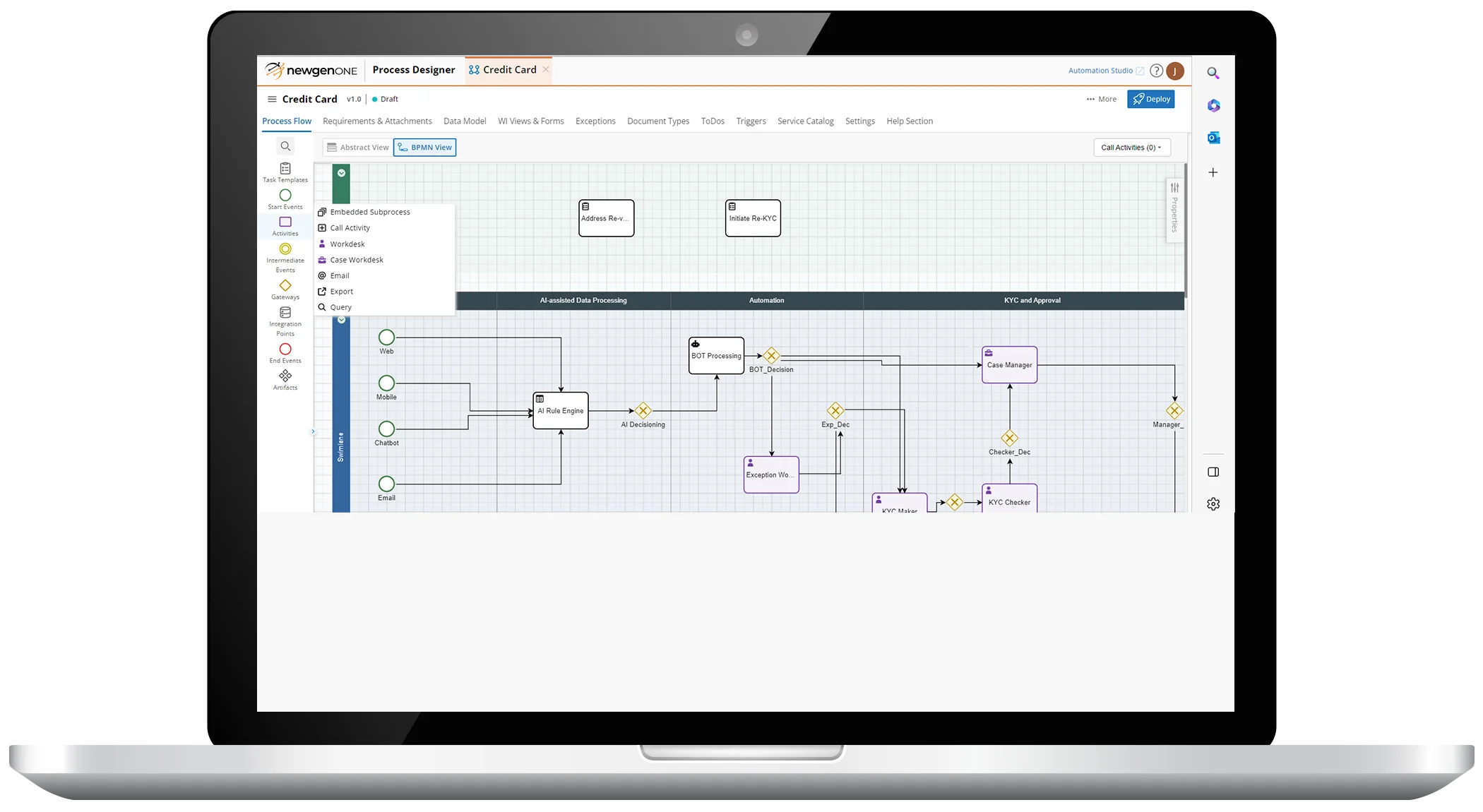
Intelligent Process Automation Capabilities of NewgenONE Platform
Lead with an Industry-recognized Platform
All You need to know about Intelligent Process Automation
Business process re-engineering is a strategic approach that changes the way businesses operate. The approach involves analyzing and redesigning existing processes to significantly improve efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction. The approach challenges traditional methods and embraces innovative technologies and practices to become leaner, agile, and more customer-centric. The goal of the approach is to optimize workflows, drive better outcomes, and gain a competitive advantage in today’s business landscape.
Business Process Management (BPM) is a holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of the clients. It promotes efficiency and effectiveness while striving for innovation, flexibility, and constant optimization of processes.
A business process management software is a process automation tool that helps organizations bridge enterprise-wide silos and streamlines their end-to-end processes and workflows. Organizations can model, analyze, monitor, optimize, and automate workflows with business process management software. It aims to increase efficiency, agility, and output in daily business operations.
BPM platforms have seen wide adoption by enterprises globally and are an intuitive must-have for any organization seeking to remain competitive in today’s modern digital world.
Organizations can automate team, departmental, and enterprise-wide business processes using a BPM framework. For example – banks have automated and standardized new borrower onboarding processes. Insurance companies use BPM to automate claims management. Some other notable examples would be –
- Employee Onboarding
- Vendor Onboarding
- Leave Approval
- Expense Approval
- Claims Processing
- Retail Lending
- Corporate Lending
- Trade Finance
- Customer Onboarding
- Task Management
- Many more
Business Process Automation offers organizations multiple benefits, ranging from cost reduction to time savings. Automation of processes leads to standardization, traceability, and compliance. Automated processes help improve the output quality, employees’ productivity, and turnaround time.
Here are a few benefits of using process modeling:
- End-to-end visibility into processes
- Process improvement and agility
- Business orchestration and efficiency
- Standardization across departments
Process modeling helps enterprises continuously improve processes with a systematic approach and facilitate periodic testing of waters for course adjustment.
Process modeling is a way to streamline workflows by creating an analytical and graphical representations of business processes. It involves data visualization where all process steps are mapped and configured to execute the desired flow.
Process modeling software helps design simple and complex business processes using a web-based drag-and-drop process modeler, which provides different contextual views of each process to enable collaboration and consensus. It often serves as the layer for orchestrating user interfaces, data models, business rules, routing decisions, etc.
Process lifecycle management is an integrated approach to managing the entire lifecycle of a process, from its conception and design, to execution, monitoring, and optimization, and its eventual retirement or replacement. This approach involves leveraging technology such as process automation, Business Process Management (BPM) software, and data analytics to streamline operations, improve productivity, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
For instance, insurance companies need to manage multiple processes, such as policy issuance, claims processing, and underwriting. They can automate and streamline the workflow of these processes by implementing a process lifecycle management solution, from initial data capture to final pay-out or settlement.
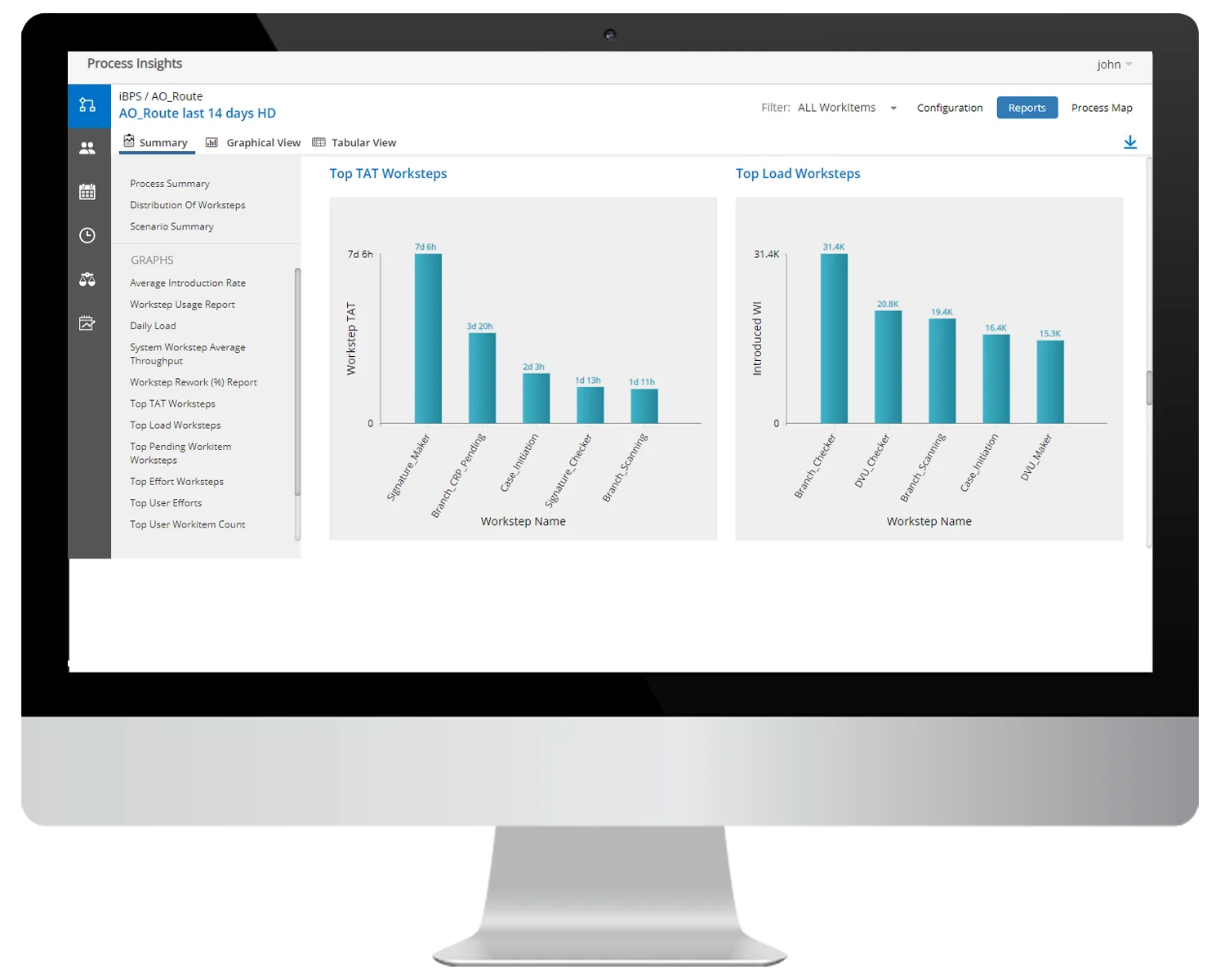
Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) involves monitoring and analyzing KPIs and other metrics to gain real-time insights into the performance of business processes. It is an essential part of Business Process Management (BPM). It captures data from various sources to analyze and provide real-time view of business operations to help organizations identify and address performance issues in real-time, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced costs.
In the context of transportation industry businesses can use BAM to monitor various Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as shipment status, delivery times, transit times, freight costs, and more. BAM would collect data from various sources such as Global Positioning System (GPS) trackers, warehouse management systems, and other logistics software systems.
Structured data is often stored in databases or data warehouses and can be easily queried and processed using traditional data analysis tools. Examples of structured data include customer information, transaction data, and inventory data.
Unstructured data, on the other hand, is often stored in non-tabular formats such as document, audio, and video files. It can be more challenging to process and analyze because it does not follow a predefined structure or format. However, advancements in new-age technologies like machine learning and natural language processing have made it possible to extract insights from unstructured data, such as sentiment analysis of customer feedback or image recognition in medical imaging.
A Business Rules Engine (BRE) is a software tool that is used to define, manage and execute business rules within an organization.
It is a statement that defines a specific aspect of the business and how it should operate. These rules can be used to automate decision-making processes, validate business transactions, and enforce business policies.
For example, a business rule might define how a customer’s credit rating is determined.
BREs are designed to be flexible and easily configurable so that business users can modify the rules without requiring assistance from IT staff. This allows the rules to be updated quickly in response to changes in the business environment.
It also enables non-technical users to manage and update the rules, which can be useful for organizations that have a lot of rules or need to modify them frequently.
BREs can be integrated into a wide range of applications, such as customer relationship management systems, enterprise resource planning systems, and financial systems.
Once the business rules are defined, the BRE evaluates the rules against the data that it receives, and takes appropriate action based on the outcome of the evaluation. This can include sending an alert, initiating a workflow, or updating a database. The BRE can also provide feedback on the results of the rule evaluation, which can be used to analyze and improve business processes.
In the context of insurance, businesses could leverage a BRE to automate the decision-making process for insurance claims processing. The rule engine would be programmed with the company’s business rules and policies, such as coverage limits, deductibles, and eligibility criteria. When a new insurance claim is submitted, the BRE would analyze the data provided in the claim form and determine the appropriate action to be taken based on the business rules and policies.
Business Process Automation (BPA) is the use of technology to automate and streamline business processes. BPA is designed to improve efficiency, reduce errors, increase speed and accuracy, and therefore free up employees to focus on more value-adding tasks. The goal of BPA is to improve overall productivity, reduce costs, and increase customer satisfaction by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks. BPA can be applied to a variety of business functions, including sales and marketing, human resources, finance and accounting, customer service, and supply chain management.
Banks could use BPA to automate the loan application process, from initial application to loan disbursement. The software could be programmed to perform various tasks, such as screening applications for eligibility, collecting required documentation, and evaluating creditworthiness.
A Business Process Management (BPM) system is a software solution that helps organizations design, model, execute, monitor, and optimize their operational processes. It provides an integrated and unified platform for automating and managing various business activities, from simple tasks to complex workflows.
The primary objective of a BPM system is to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes, enhance customer experience, increase the agility of operations, and reduce costs.
The main features and capabilities of a BPM system include:
- Process modeling and design: It allows users to create visual representations of business processes, including process maps, flowcharts, and diagrams.
- Workflow automation: It enables the automatic execution of business processes, thereby reducing manual intervention and errors.
- Process monitoring and analytics: It provides real-time insights into the performance of business processes, thereby helping organizations to identify bottlenecks, resolve issues, and make informed decisions.
- Task management: It helps organizations allocate and manage tasks among team members, thereby ensuring timely and efficient completion of work.
- Rule-based decision-making: It provides a framework for automating decisions based on pre-defined rules and conditions.
Process analytics is the analysis of business processes to improve their efficiency, effectiveness, and overall performance. This involves collecting and analysing data from various sources, such as business systems and transactional data, to gain insights into how processes are performed and identify areas for improvement. The insights generated from process analytics can be used to optimize business processes, reduce costs, increase productivity, and improve customer satisfaction. The goal of process analytics is to provide valuable insights into the performance of business processes.
Banks could use process analytics to monitor and analyze their credit card transactions in real-time. The analytics software can be programmed to identify suspicious transactions, such as those that are outside the customer’s typical spending patterns, occur in unusual locations, or involve large amounts.
Business Process Orchestration (BPO) software helps in the coordination and automation of multiple business processes. These orchestrated processes offer better efficiency. By leveraging the business process orchestration system, you can bring together data from multiple processes, systems, and applications to provide a synchronized and coordinated output. The software can orchestrate inputs from multiple data sources such as tasks, processes, databases, bots, decision engines, APIs, etc. With business process orchestration, businesses can become more agile, efficient, and customer-focused and also reduce costs and increase profitability.
Banks could use BPO to orchestrate the various tasks involved in mortgage loan processing, from initial application to loan disbursement. The software can be programmed to coordinate the different departments involved in the loan process, such as underwriting, credit analysis, document processing, and closing.
Process gamification is the application of game design elements to a business process to make it more engaging and motivating. The use of game mechanics such as points, levels, badges, leaderboards, and challenges can help drive behavior, increase engagement, and create a sense of competition.
To gamify a business process, you first need to identify the process you want to gamify and set clear goals for what you want to achieve. The next step is to choose game mechanics that align with your goals and design the game framework accordingly. Test the game with a small group of people, refine it as needed, and then launch and promote it to your target audience. Finally, you can monitor the game’s progress and analyze the data to identify areas for improvement. Gamifying a business process should have a clear purpose and be aimed at making the process more engaging and motivating, not just adding a game-like layer to it.
Process gamification can improve process efficiency by boosting employee engagement and motivation, which can lead to better performance, productivity, and quality.
It can also provide real-time feedback, recognition for achievements, and encourage learning and development.
By using process gamification, insurance companies can make the training process more engaging and interactive, thereby helping keep new agents motivated and invested in their development. It also provides a more effective and efficient way of delivering training, thereby improving the pace at which new agents are market ready.
Human-centric BPM workflow is an approach to designing and managing business processes that focuses on the needs and experiences of the people who interact with those processes. It places humans at the center of process design, recognizing that the success of any business process ultimately depends on the people who use and manage it. Human-centric workflows allow organizations to create workflows that provide a workdesk to humans to manage exceptions and sequential approve/reject tasks.
Business Rules Management (BRM) is the process of managing and automating the business rules used to make decisions in an organization. Business rules are specific guidelines or criterias that help an organization make decisions on how to operate or how to respond to certain situations. For example, a rule might dictate that a customer must be notified if their payment is overdue by more than 30 days. By using BRM, organizations can store and manage their business rules in a centralized system, making it easier to ensure consistency and accuracy in the decision-making process.
Business Process Orchestration (BPO) is the use of multiple automation technologies to achieve a specific process outcome. The process implies designing, monitoring, and optimizing complex end-to-end processes involving multiple systems, applications, and stakeholders. For example, BPO can be implemented in the process of issuing a passport to a citizen. When a citizen applies for a passport, the procedure involves different processes and systems, including identity verification, document processing, fee collection, and passport printing.
By implementing BPO, all these processes can be orchestrated to work together seamlessly. For instance, when a citizen submits their application, BPO can automatically initiate the identity verification process using the government’s citizen record database. Following this stage, the document processing system can be automatically notified and start processing the application. Once the application is approved, BPO can initiate the process of fee collection and finally start with the passport printing process.
Business process management has applications across various industries and use cases. Some common examples include:
- Customer Onboarding: BPM can automate the customer onboarding process, to ensure a smooth and efficient experience from application submission to approval.
- Claims Processing: Insurance companies use BPM to streamline and accelerate their claims processing, thereby reducing manual effort and improving accuracy.
- IT Service Management: BPM helps manage IT service requests, incidents, and changes, to ensure a timely resolution and minimize downtime.
Business Process Management helps users understand, streamline, and improve their business processes. It enables the automation of workflows, and allows for smoother operations. It provides visibility into process performance and metrics, thereby aiding informed decision-making. It also enhances collaboration and communication to foster teamwork. It ensures compliance with regulations and supports continuous process optimization. Overall, BPM empowers businesses to work more efficiently and adapt to changing demands.