Why Intelligent RPA Matters for Enterprise-scale Automation
Standalone RPA automates individual tasks but lacks the process intelligence required to scale automation across end-to-end workflows. As complexity increases, gaps emerge around exception handling, audit controls, and usability. Newgen’s RPA embeds bots within enterprise processes and applies bot and process intelligence to manage exceptions, involve humans where judgment is needed, and enforce governance at scale. This enables intelligent, context-aware automation across onboarding, claims processing, service request management, accounts payable, and other cross-functional processes.
What Differentiates NewgenONE RPA in Enterprise Automation?
End-to-end Process Automation for Enterprise-scale Operations
- Leverages AI and GenAI–enabled RPA to extend automation beyond isolated tasks into end-to-end enterprise processes.
- Enables intelligent automation of repetitive and rule-based work while maintaining process context across multi-step workflows.
- Allows bots to operate both independently at the task level and embedded within large, complex enterprise processes.
- Bridges task automation and process execution, supporting scalable automation across cross-functional operations.
Hybrid Workforce Orchestration for Enterprise Workflows
- Brings humans and bots together within a single workflow using the process designer to orchestrate seamless user journeys.
- Enables process owners to delegate repetitive and rule-based tasks to bots for consistent execution.
- Allows humans to focus on complex decisions and judgment-driven activities.
- Supports decision handling through built-in case and exception management within the same process flow.
AI-driven Process Diagnosis for Scalable Automation
- Leverages AI-driven process insights to assess the health and performance of complex enterprise processes, enabling data-backed optimization decisions.
- Surfaces hidden bottlenecks and inefficiencies within process flows that affect cycle time, and automation execution.
- Determines activities best suited for bot execution, helping enterprises focus automation efforts where they deliver the most value.
- Forecasts future resource and capacity requirements using historical process data, supporting proactive planning and scalable automation outcomes.
Enterprise-grade RPA Governance and Control for Compliance
- Provides centralized visibility into bot health, availability, performance, and execution status across enterprise environments.
- Maintains detailed audit logs and discrepancy tracking to support compliance, traceability, and controlled automation.
- Enables enterprises to scale automation dynamically by cloning bots and scaling up or down based on workload and usage.
- Secures sensitive information through a centralized credential vault, simplifying environment upgrades while protecting confidential data.
What Enterprise-grade RPA Capabilities Does the NewgenONE Platform Offer?
Low-code Bot Scripting Studio
Intelligent Document Processing
Bot Control Centre for Enterprise Operations
Intelligent Enterprise Communication Automation
Non-invasive Integration for Existing Systems
Enterprise-grade Exception Management
AI-driven Hyper-vigilant Virtual Workforce
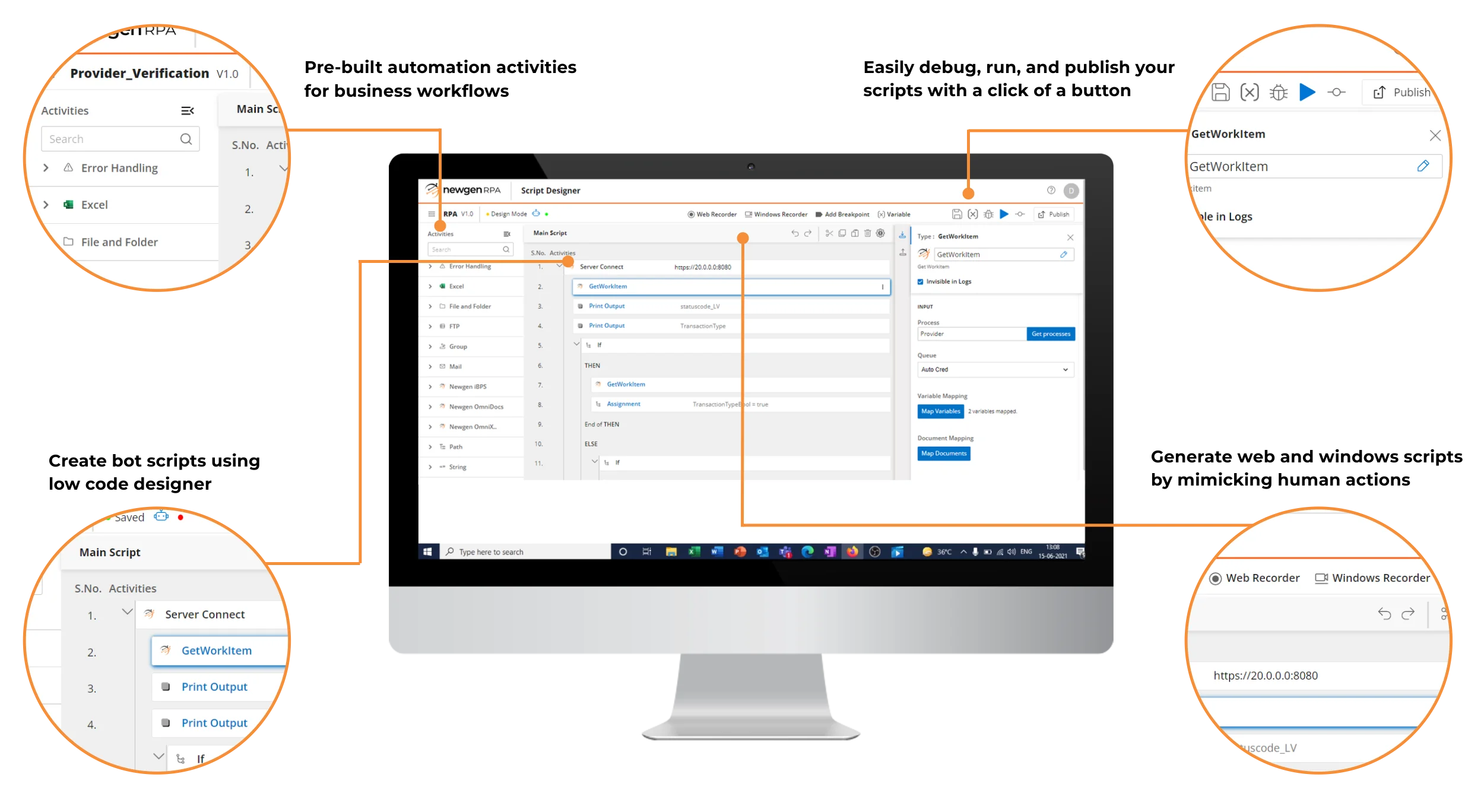
Low-code Bot Scripting Studio
- Enterprise-grade, low-code bot design environment that enables seamless collaboration between business and IT teams to record, debug, and execute automation scripts across web and Windows applications, supporting modern automation strategies.
- Drag-and-drop automation design using a configurable activity catalog, allowing teams to build automation sequences for business use cases without writing code, improving productivity and speed of delivery.
- Supports creation of advanced, dynamic, and reusable automation workflows using a rich set of pre-built activities,including browser automation, file and folder operations, Excel, email, FTP, date and time functions, and error handling, designed for enterprise-scale execution.
Intelligent Document Processing
- Strong AI-based capabilities in imaging, document extraction, redaction, and classification along with native document management to handle intelligent document processing use cases
- Automatic classification and extraction of documents with AI-based bots to achieve straight-through-processing of complex document-based business processes, such as invoice processing, trade finance
- Extends document intelligence to unstructured interaction data, using AI-based bots to sense and interpret customer communications across social channels and deliver context-aware responses.
Bot Control Centre for Enterprise Operations
- Enterprise-grade control and monitoring of machines, bots, jobs, vaults, and users in real time, enabling automation managers to govern bot execution, performance, licensing, and data security from a centralized environment.
- Centralized interface for real-time bot monitoring and intelligent scaling, enabling controlled upscaling and downscaling of bots across automated operations.
- RPA bot’s advanced multitasking capabilities allow it to run multiple non-UI jobs in parallel, drastically reducing the time required to complete complex workflows.
Intelligent Enterprise Communication Automation
- Automate incoming emails using AI-based bots that read, understand, and respond to messages without altering or losing the original content, while recognizing email patterns and context to trigger business transactions in third-party systems.
- Sense and respond to customer interactions across social channels such as Twitter and Facebook using AI-based bots that recognize context and deliver timely, relevant responses.
Non-invasive Integration for Existing Systems
- Automation of legacy systems like Mainframe AS400 with Newgen RPA by leveraging desktop automation to enable enterprises push and pull data from legacy terminals.
- Enable non-invasive integration across diverse legacy and third-party applications, including data extraction from external systems, MS Excel handling, PDF manipulation, reconciliation, and reporting.
Enterprise-grade Exception Management
- Manage automation exceptions efficiently using pre-built error-handling activities in the RPA scripting studio, integrated with the iBPS exception handling mechanism for cost-effective resolution.
- Handle incoming exceptions and cases seamlessly through in-built case management tightly coupled with RPA to manage diverse exception scenarios end to end.
AI-driven Hyper-vigilant Virtual Workforce
- Accelerate enterprise processes with unattended RPA by deploying bots as an always-on, scalable virtual workforce operating 24×7 for intelligent automation.
- Automate repetitive, rule-based tasks using RPA bots, freeing employee bandwidth for higher-value, decision-driven work while reducing operational risk and human error.
Low-code Bot Scripting Studio
- Enterprise-grade, low-code bot design environment that enables seamless collaboration between business and IT teams to record, debug, and execute automation scripts across web and Windows applications, supporting modern automation strategies.
- Drag-and-drop automation design using a configurable activity catalog, allowing teams to build automation sequences for business use cases without writing code, improving productivity and speed of delivery.
- Supports creation of advanced, dynamic, and reusable automation workflows using a rich set of pre-built activities,including browser automation, file and folder operations, Excel, email, FTP, date and time functions, and error handling, designed for enterprise-scale execution.
Intelligent Document Processing

- Strong AI-based capabilities in imaging, document extraction, redaction, and classification along with native document management to handle intelligent document processing use cases
- Automatic classification and extraction of documents with AI-based bots to achieve straight-through-processing of complex document-based business processes, such as invoice processing, trade finance
- Extends document intelligence to unstructured interaction data, using AI-based bots to sense and interpret customer communications across social channels and deliver context-aware responses.
Bot Control Centre for Enterprise Operations

- Enterprise-grade control and monitoring of machines, bots, jobs, vaults, and users in real time, enabling automation managers to govern bot execution, performance, licensing, and data security from a centralized environment.
- Centralized interface for real-time bot monitoring and intelligent scaling, enabling controlled upscaling and downscaling of bots across automated operations.
- RPA bot’s advanced multitasking capabilities allow it to run multiple non-UI jobs in parallel, drastically reducing the time required to complete complex workflows.
Intelligent Enterprise Communication Automation

- Automate incoming emails using AI-based bots that read, understand, and respond to messages without altering or losing the original content, while recognizing email patterns and context to trigger business transactions in third-party systems.
- Sense and respond to customer interactions across social channels such as Twitter and Facebook using AI-based bots that recognize context and deliver timely, relevant responses.
Non-invasive Integration for Existing Systems

- Automation of legacy systems like Mainframe AS400 with Newgen RPA by leveraging desktop automation to enable enterprises push and pull data from legacy terminals.
- Enable non-invasive integration across diverse legacy and third-party applications, including data extraction from external systems, MS Excel handling, PDF manipulation, reconciliation, and reporting.
Enterprise-grade Exception Management

- Manage automation exceptions efficiently using pre-built error-handling activities in the RPA scripting studio, integrated with the iBPS exception handling mechanism for cost-effective resolution.
- Handle incoming exceptions and cases seamlessly through in-built case management tightly coupled with RPA to manage diverse exception scenarios end to end.
AI-driven Hyper-vigilant Virtual Workforce

- Accelerate enterprise processes with unattended RPA by deploying bots as an always-on, scalable virtual workforce operating 24×7 for intelligent automation.
- Automate repetitive, rule-based tasks using RPA bots, freeing employee bandwidth for higher-value, decision-driven work while reducing operational risk and human error.
Intelligent Process Automation Capabilities of NewgenONE Platform
Lead with an Industry-recognized Platform
All you need to know about Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is used to automate manual, labor-intensive, time-consuming, rule-based, or repetitive tasks. Typically, a bot performs these tasks more efficiently than humans while also being available 24/7 and easily interacting with in-house applications, websites, and user portals. Bots work well in a static environment and can log into different applications, copy and enter data, open emails and attachments, carry out calculations, and much more.
RPA, if implemented well, can yield tremendous tactical and specific outcomes for enterprises across industries. RPA can empower your employees to perform better by automating mundane routine tasks to free up their bandwidth for more value-added tasks. Furthermore, intelligent RPA can help you predict behaviors and drive experience across touchpoints in the customer journey.
There are two main types of RPA:
- Attended RPA – Robots act as personal assistants on users’ computers, performing a series of user-triggered actions to complete simple, repetitive tasks and streamline the workflow
- Unattended RPA – Robots require little to no human intervention while executing complex functions, such as intensive data processing, data management, or even complete back-office functions
Some key use cases of RPA include:
- Report generation: RPA can be used to automate the generation of reports by pulling data from multiple sources, formatting it, and creating reports in various formats such as PDF or Excel.
- Data entry and migration: RPA can be used to automate the process of entering data into forms, spreadsheets, or databases, as well as migrating data from one system to another.
- Invoice processing: RPA can be used to extract data from invoices and receipts, validate it, and then update accounting systems.
- Customer service: RPA can assist in customer service tasks such as answering queries, updating customer data, and processing refunds or returns.
- Compliance monitoring: RPA can assist in compliance monitoring by automatically tracking and reporting regulatory changes, ensuring adherence to industry standards, and detecting fraudulent activities.
Bot scripting is a key aspect of robotic process automation. It is a technology that allows software robots, or “bots,” to automate routine and repetitive tasks that were previously performed by humans. Bot scripting involves creating a set of instructions or commands that the bot will follow to complete a specific task or process.
In RPA, bots can be programmed to interact with various applications, systems, and websites using scripting languages and Application Programming Interface (APIs). Bot scripting involves writing code or configuring pre-built modules to define the actions that the bot will perform. The script may include commands such as logging into an application, extracting data from a document, entering data into a form, clicking buttons, and navigating through menus.
For example, by automating claims processing using bot scripting, insurance organizations can reduce manual errors, improve customer satisfaction, and accelerate claims processing time.