Leverage web-based business rules management system to define business policies and procedures and keep the decision logic separate from the whole application logic. Define, control, change, and deploy rules that govern critical business operations for greater agility and control with the least impact on the business logic. This helps automate the repeatable decisions that control the business and define an organization’s strategy.
Business Rules Management Capabilities of NewgenONE Platform
Simplified Rule and Rule flow Creation
Creation and execution of simple to complex business rules using decision tables and if-else-based logic statements
GenAI-assisted configurable rule flow definitions for conditional execution of rules
Visual representation of rule flows to track the flow and order of execution
Ability to add new or use pre-built functions for faster designing of business rules by leveraging AI
Enable Rule Management and Versioning
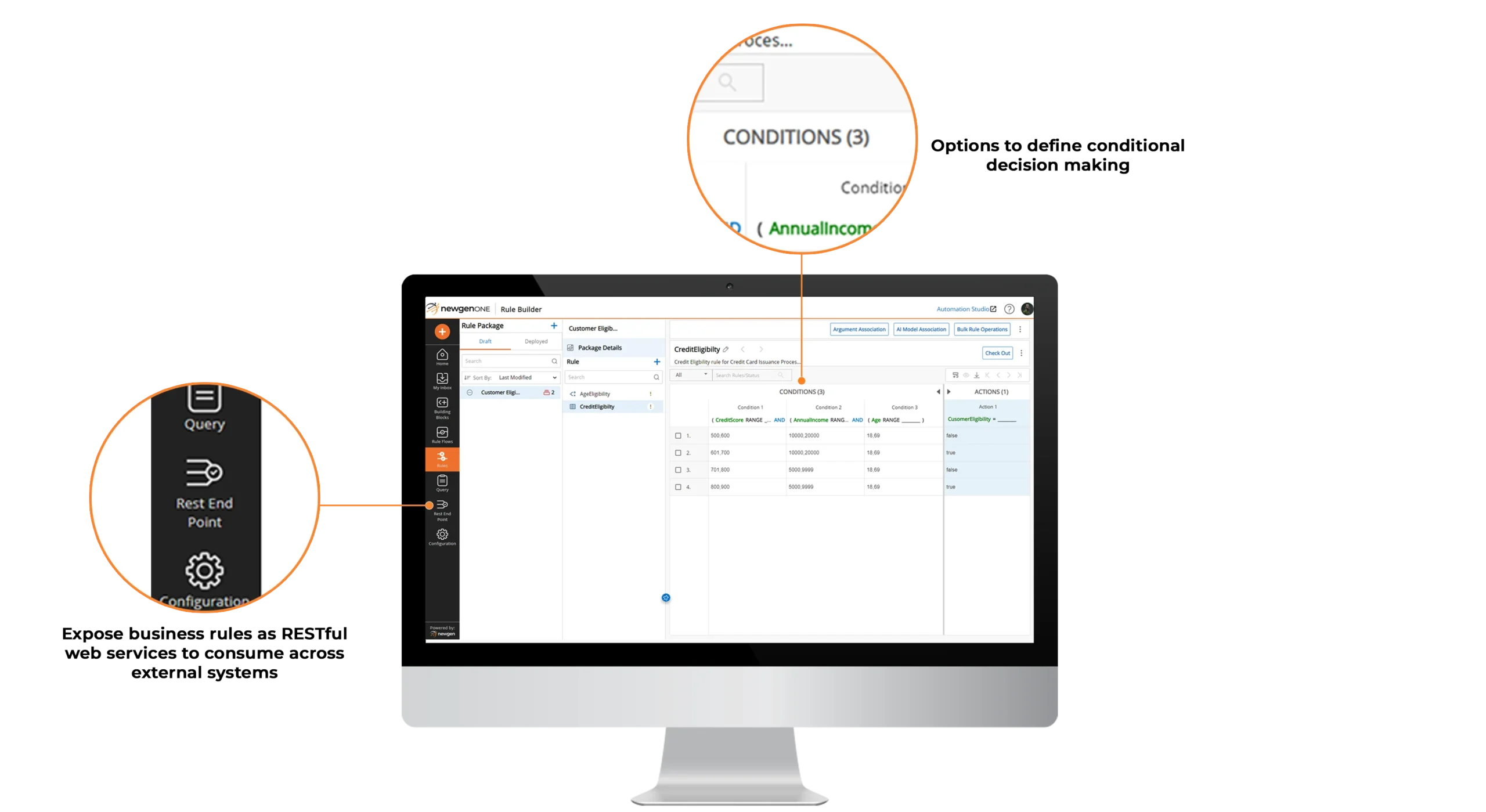
Customized conditions for rule application based on specific needs and priority
Version management of defined rules and rule flows for easier tracability on changes
Empower Rule Reusability
Out-of-the-box, industry, and function-specific business rules library to speed up implementation
Reusable rule definitions that can be used across activities, processes, and business applications
Rule and ruleflow available as web service for easy integration with third-party applications
Rule Extensibility
Ability to fetch data in real-time from database tables using a dynamic picklist for improved accuracy in rule execution
Decision Model and Notations (DMN) for standardized way to model and represent business decisions in visual flows for easier understanding of stakeholders
Intelligent decision-making through predictive AI models
Rule Analysis and In-flight Changes
Ability to analyze rules before deployment to verify logical consistency by leveraging AI models
Use GenAI intuitively to make real-time modifications based on business needs
Inflight testing, validation, and verification of business rule
Intelligent Process Automation Capabilities of NewgenONE Platform
Lead with an Industry-recognized Platform
All You need to know about Business Rules Management (BRM)
Business Rules Management (BRM) is the process of managing and automating the business rules used to make decisions in an organization. Business rules are specific guidelines or criterias that help an organization make decisions on how to operate or how to respond to certain situations. For example, a rule might dictate that a customer must be notified if their payment is overdue by more than 30 days. By using BRM, organizations can store and manage their business rules in a centralized system, making it easier to ensure consistency and accuracy in the decision-making process.
A Business Rules Engine (BRE) is a software tool that is used to define, manage and execute business rules within an organization.
It is a statement that defines a specific aspect of the business and how it should operate. These rules can be used to automate decision-making processes, validate business transactions, and enforce business policies.
For example, a business rule might define how a customer’s credit rating is determined.
BREs are designed to be flexible and easily configurable so that business users can modify the rules without requiring assistance from IT staff. This allows the rules to be updated quickly in response to changes in the business environment.
It also enables non-technical users to manage and update the rules, which can be useful for organizations that have a lot of rules or need to modify them frequently.
BREs can be integrated into a wide range of applications, such as customer relationship management systems, enterprise resource planning systems, and financial systems.
Once the business rules are defined, the BRE evaluates the rules against the data that it receives, and takes appropriate action based on the outcome of the evaluation. This can include sending an alert, initiating a workflow, or updating a database. The BRE can also provide feedback on the results of the rule evaluation, which can be used to analyze and improve business processes.
In the context of insurance, businesses could leverage a BRE to automate the decision-making process for insurance claims processing. The rule engine would be programmed with the company’s business rules and policies, such as coverage limits, deductibles, and eligibility criteria. When a new insurance claim is submitted, the BRE would analyze the data provided in the claim form and determine the appropriate action to be taken based on the business rules and policies.
A Business Rules Management System (BRMS) offers several benefits to organizations:
- Centralized Rule Management: BRMSs provide a centralized platform for creating, storing, and managing business rules. This ensures consistency and eliminates redundancy across different applications and systems.
- Scalability: BRMSs allow organizations to scale their business rules as needed, accommodating changes in business processes, regulations, and market conditions without requiring significant manual effort.
- Agility and Flexibility: BRMSs enable rapid adaptation to changing business requirements by separating business rules from application code. This allows organizations to modify rules quickly and deploy them without disrupting existing systems.
- Improved Compliance: BRMSs help ensure regulatory compliance by enforcing consistent application of rules across the enterprise. They also provide auditing and reporting capabilities to track rule changes and demonstrate compliance to regulatory authorities.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By automating decision-making based on predefined rules, BRMSs streamline business processes, reduce manual errors, and improve operational efficiency.
- Empowered Business Users: BRMSs empower business users and domain experts to define and manage business rules without extensive IT involvement. This democratization of rule management speeds up decision-making and enhances agility.
- Increased Consistency and Accuracy: BRMSs enforce consistent application of rules across systems, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies in decision-making. This leads to improved data quality and reliability.
- Cost Savings: BRMSs can lead to cost savings by reducing the time and effort required for manual rule implementation, maintenance, and updates. They also contribute to faster time-to-market for new products or services.
Overall, a Business Rules Management System (BRMS) helps organizations achieve greater agility, compliance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in managing and implementing business rules across the enterprise.