Simplify the complete invoice lifecycle, from capture to payment while minimizing manual hand-offs and expediting turnaround time. Streamline workflows with a low-code, AI-enabled solution that maximizes efficiency across finance operations. Empower your users to effortlessly establish control over cash and working capital through real-time analytics and performance dashboards. Leverage Generative AI (GenAI), Large Language Models (LLMs), and Machine Learning (ML) to identify inconsistencies, manage intricate tax structures, and gain predictive insights for informed decision-making. Enable timely payments, improve payment incentives, and enhance vendor collaboration to build stronger relationship. Ensure trust and transparency with auditable, bias-free automation with the Newgen TrustAI layer.
Explore What Newgen’s AI-powered Invoice Management Solution Can Do for You
Multi-channel Invoice Capture and Smart Data Extraction
Capture and extract invoices from multiple sources, including paper, email, and portals, using OCR and advanced data extraction. Ensure accuracy by automatically reading and processing invoice details from every source
Automated Workflows and Approval Management
Streamline the invoice lifecycle with dynamic, rule-based workflows that automatically route submissions for review and approval. Reduce processing time by eliminating manual hand-offs and expediting decision-making
Centralized Document Repository and Secure Archival
Store and manage all invoice-related documents in a single, secure repository. Get quick access and retrieve records while maintaining compliance with audit and regulatory requirements
Fraud and Duplicate Invoice Detection
Leverage AI-driven fraud detection that identifies and flags duplicate or fraudulent invoices. Minimize financial discrepancies and protect your organization against errors and fraud
Real-time Analytics and Performance Dashboards
Gain complete visibility into the accounts payable process with intuitive, real-time dashboards. Monitor invoice statuses, track supplier performance, and generate actionable insights for simplified financial management
Seamless ERP Integration and Touchless Processing
Integrate with ERP and financial systems, such as SAP and Oracle, for a truly touchless processing experience. Reduce data silos and streamline the end-to-end invoice management process
Approval Hierarchies and Exception Handling
Customize approval workflows to organizational needs with configurable hierarchies and escalation rules. Leverage smart exception handing to flag non-compliant invoices without slowing down overall processing
Relationship Management and Performance Insights
Track supplier/vendor performance, manage dynamic discounting, and ensure timely, accurate payments. Empower finance teams with real-time insights and collaborative tools to strengthen stakeholder relationships
AI-driven Innovation at the Core
Automation and Productivity Agent–NewgenONE Marvin
Pre-loaded queries and rapid insights
Automated header and line-item extraction
Instant data summarization for smarter decisions
Agentic AI Shield
Ethical AI and continuous monitoring
Responsible practices for full accountability
Robust data security with regulatory compliance
Trusted AI
Fully auditable, interpretable workflows
Secure model deployment with role-based access control
Configurable models with internal data from trusted sources only
Brands using NewgenONE Platform



Explore Other Solutions Built on NewgenONE Platform for Finance and Accounting
All you need to know about Accounts Payable Automation Software
An AP platform is a platform that allows for invoice processing. The platform includes tools, infrastructure, and other features, that are in accordance with the set expectations.
An ideal accounts payable system automates the end-to-end invoice processing, reduces manual work, streamlines approval workflows, manages payments, and improves compliance adherence, leading to cost and time savings for businesses.
The capabilities of accounts payable software include enablement of source acquisition, duplicity validation, data correctness validation, and follow-through of the approval cycle to ensure that the right payment is done.
Accounts payable automation involves the digitization of all payable transactions, including invoices, debit notes, credit notes, and other such similar transactions, that affect the finances of an organization. Invoice automation is essential as it involves the outflow of money, which has a direct impact on the cash-balance of an organization.
The primary objective of accounts payable invoice automation is to achieve compliance and optimize operational cost per invoice processing.
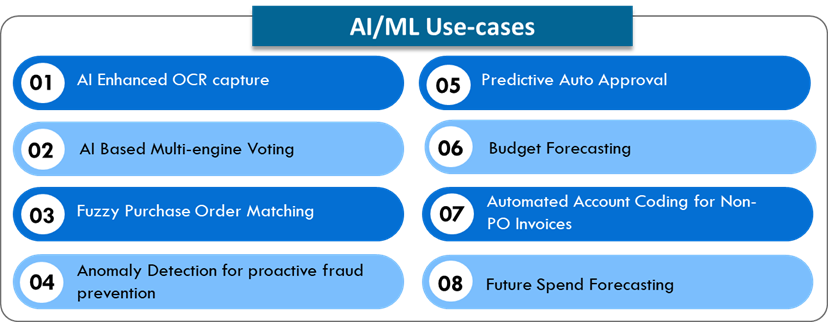
The factors for vendor selection, as documented in the APIA market guide by Gartner, include intelligent optical character recognition (OCR) capture, machine–readable invoices, account coding suggestions, fuzzy PO matching, duplicate detection, supplier portal, advanced analytics, integrations, supplier discounting, payment, and digital mailroom capabilities.
A machine-readable invoice refers to automatic data capture from the invoice documents, using a software, without any human intervention.
While processing non-material invoices (also called non-PO invoices), the processing user is required to provide account and cost centre codes (also termed as coding) for booking the expense as contra for the vendor codes. This is an absolute necessity, and many times, the users, in their hurry to complete the invoice submission transaction, end up providing non-applicable information as well. This results in a month/quarter-end process called reconciliation, which only adds to the manual effort of correcting the wrongly entered details.
In order to improve the accuracy of coding, historical trend-based suggestive codes are displayed for the user. The user can select the appropriate codes and help considerably reduce the effort of month/quarter-end activities. This also enhances real-time visibility of the ledger balance, as wrong coding is avoided.
Matching refers to invoice content matching with Purchase Order (PO) and, wherever applicable, with goods receipt, which are also termed as Goods Received Note (GRN). Matching implies the exact details between all 2 or 3 of the documents. However, in certain cases, the product/item or service name may have detailed, additional, actual, or translated names, which can result in non-matching.
To avoid this, a list of values is maintained for each PO line-item information, on how vendors represent them in their invoices. While matching, the system should look for different aliases for PO line information in invoices and goods receipts and then provide effective matching, rather than making the users do them manually.
The above is just one of the use-cases. There are multiple other needs that can be provided for fuzzy PO matching.
Duplicate invoices are typically an exact availability for vendor code, invoice number, invoice date, and invoice amount. A fuzzy check also helps in some invoices getting user inputs that differentiate duplicates, like adding a special charter to the invoice number, which should not be done.
In order to ensure a high level of risk observation for duplicate invoices, Newgen has an exact match and a partial match observation display. The partial match display could be on any 3 or 2 fields. This identification helps the user ensure that the right invoices are passed.
A supplier portal is a marketplace kind of solution in which vendors/suppliers are onboarded with their offerings – products, and services, with various other parameters. This helps organizations determine the most appropriate potential vendor for supplying to them.
The key benefits of invoice processing software can be classified into two parts – tangible and intangible. Both parts are related to the cost aspect of processing.
An end-to-end invoice processing software helps in better visualization for liability planning, compliance with Standard-Operating-Procedures (SOPs), and complete auditability of who-what-when-how to reduce non-compliance.
Invoices can be classified based on the type of material or services or others that are a part of the procurement.
Different types of invoices include material, non-material, services, advance, capital goods, general services, utilities, and much more.
The key features of accounts payable software include:
- Omnichannel acquisition of invoices at the point of entry using AI
- Machine reading of the content
- Data validation with underlying applications (PO, GRN, etc)
- Exception management
- AI-assisted Approval
- GenAI-powered submission and archival
- Dashboards for operations, business, technology, and strategies
- Seamless integration for unified processing
An Accounts Payable (AP) automation tool refers to a technology suite that helps in the automation of invoice processing as per the current governance/compliance model depicted in the Standard-Operating-Procedures (SOPs). The extent of the automation and the outcome–focused features help in differentiating the solutions.
AP automation involves a set of tools configured to make a transaction flow from start to end and perform archival as required and documented in the SOP. The typical working model of AP automation includes omnichannel initiation, machine reading, validations, approvals, and submission to ERP, following which the contents and the data are archived for long-term reference as per regulations.
Accounts Payable (AP) involves the outflow of money from an organization, which considerably raises the validation risks.
The three major aspects of accounts payable system include:
- Visibility –It ensures accurate reporting of the SOP activities so that optimal planning can be done for cash flow/liability
- Audit and compliance –It ensures that future audits do not result in non-compliance, which can lead to penalties
- Cost –It analyses the potential areas that will help in optimization, productivity, and efficiency, resulting in reduced bottom line per invoice processing
Accounts payable (AP) process automation involves the digitization of all accounts payable transactions, including invoices, debit notes, credit notes, and other such similar transactions, which affect the finances of an organization. Accounts payable automation is essential as it involves the outflow of money, which has a direct impact on the cash balance of an organization.
The key features of accounts payable software include:
- Omnichannel acquisition of invoices at the point of entry
- Machine reading of the content
- Data validation with underlying applications (PO, GRN, etc)
- Exception management
- Approval
- Submission and archival
- Dashboards for operations, business, technology, and strategies
- Seamless integration for unified processing
An ideal Accounts Payable (AP) process automation tool refers to a technology suite that helps in the automation of invoice processing as per the current governance/compliance model depicted in the Standard-Operating-Procedures (SOPs). The extent of the automation and the outcome–focused features help in differentiating the solutions.
Accounts Payable (AP) process automation involves a set of tools configured to make a transaction flow from start to end and perform archival as required and documented in the SOP. The typical working model of AP automation includes omnichannel initiation, machine reading, validations, approvals, and submission to ERP, following which the contents and the data are archived for long-term reference as per regulations.



