Artificial intelligence (AI) has made its presence felt across all domains. The continuously evolving technology keeps tech enthusiasts and industries on the edge, making them wonder what’s next. The latest to jump onto the artificial intelligence (AI) bandwagon is Generative AI (GenAI). Its launch into the public eye was nothing short of a technological spectacle. As people marveled at machines showcasing their ‘creative flair,’ many began to take a deeper interest in the broader domain of artificial intelligence (AI). What was once seen as abstract, distant tech jargon soon became a topic of household discussion. For many, GenAI served as their gateway to understanding the expansive and transformative world of artificial intelligence (AI). The use cases and possible solutions to current business challenges that AI and its subtypes offer are incredible. In this blog, I’ll demystify these terms and delve deeper into AI vs. Generative AI, shedding light on their nuances. Happy exploring!
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Making Smart Decisions
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? When we refer to AI, we’re alluding to machines equipped with capabilities that mirror human cognitive functions, albeit in a rudimentary form. But what makes artificial intelligence (AI) such a focal point in modern technological discussions?
Learns from Experience: Just as humans accumulate knowledge through experiences, growing wiser and more skilled over the years, artificial intelligence (AI) systems refine their capabilities through constant exposure to data. It’s an iterative learning process where past mistakes guide future actions, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
Makes Informed Choices: AI can be visualized as a vast, highly organized digital brain. It can quickly sift through expansive datasets, identify patterns, and make decisions based on its findings. This ability to analyze and respond promptly makes AI an invaluable asset for modern enterprises.
Completes Tasks Quickly: In today’s data-centric world, efficiently processing information has become an absolute necessity. Artificial intelligence (AI) is adept at executing data-driven tasks—like pattern recognition or data sorting—at speeds humans can’t match.
Industries being Impacted by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the use cases:
Banking: Beyond the simplicity of transaction monitoring, artificial intelligence (AI) underpins complex financial models, helps in credit risk scoring and fraud detection, analyzes customer interactions for cross-sell/upsell, provides personalized loan offerings and even investment strategies.
Insurance: Helps classify an insurance claim as fraudulent in real-time to reduce revenue leakage and enables health insurance coverage checks and analysis of vehicle photographs.
eCommerce: AI’s role in e-commerce isn’t restricted to mere product recommendations. It optimizes supply chains, predicts inventory needs, and even aids in dynamic pricing based on real-time market demands.
Healthcare: Within medical facilities, AI’s prowess isn’t limited to scanning and interpreting medical images. It aids in prognosis, treatment recommendations, and even patient management, harnessing vast medical databases to improve patient outcomes.
Generative AI: The Digital Creator
What is Generative AI? GenAI goes a step beyond the analytical. If AI is the analytical mind, Generative AI is the imaginative one. But how does this imagination manifest?
Creates Content: GenAI’s creative potential is vast. It can emulate art styles, generate unique compositions, and even draft textual content. This is not merely replication, but a creation influenced by patterns it has previously identified.
Invents Through Simulations: GenAI doesn’t just predict—it hypothesizes. By simulating various scenarios, whether it’s the interaction of molecules for a drug or the structural integrity of a new architectural concept, it provides invaluable foresight that can guide further research or development.
Interacts in Real Time: One of GenAI’s most intriguing capabilities is its dynamic responsiveness. Whether in design tools or interactive simulations, it recalibrates outputs instantaneously based on real-time input, ensuring a seamless user experience.
Industries being Impacted by Generative AI and the use cases:
Art and Design: The collaboration between artists and GenAI isn’t just a novelty; it’s revolutionizing design paradigms, leading to innovative art forms and design patterns.
Medicine: Beyond drug interactions, GenAI facilitates the entire drug development process, from molecular design to clinical trial simulations, expediting and refining the research process.
Journalism: GenAI aids journalists in more ways than just article drafting. It can synthesize vast amounts of data to unearth trends, generate visual representations, and even suggest narrative structures.
AI vs. Generative AI. What’s the Key Difference?
Both AI and Generative AI use machine learning models to mimic human abilities. However, to understand AI vs. Generative AI, we need to understand their focus areas:
Purpose: Artificial Intelligence (AI) aims to analyze data and make decisions. GenAI, on the other hand, is all about creating fresh, new content.
Outputs: If you ask Artificial Intelligence (AI) a question, it provides an answer. But ask GenAI, and it might give you a new song, image, or story.
How They Learn: Both rely on data, but they use it differently. While Artificial Intelligence (AI) looks for the right answer, GenAI constantly refines its creative process based on what it learns.
Data Science Platforms to Harness the Power of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Keen to adopt AI/Machine Learning (ML) in your organization? To effectively use Artificial Intelligence (AI) as a competitive advantage, you must assess where you are in the data science maturity journey: Beginner, Implementer, Advancer, or Leader. The graph below can help you assess
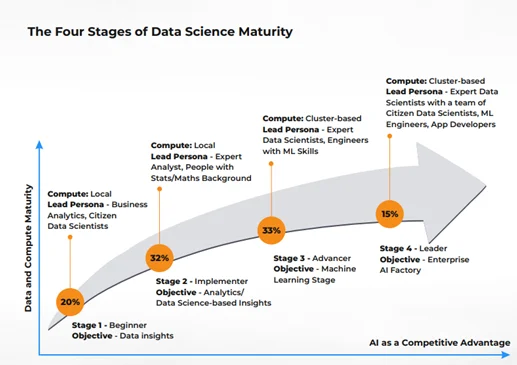
Once you level up to become an Artificial Intelligence (AI) Leader, where you are successfully incorporating insights into your business processes and use cases, you need to scale your AI adoption across the enterprise. However, this is no mean feat. It requires a substantial commitment in terms of time and resources (expertise and monetary investment).
Data Science Platforms can help fast-track the AI/ML journey by automating the entire life cycle of data science projects. Such platforms help prepare and visualize data for large ML projects, build and train ML models, and deploy and monitor these models. It increases productivity, fosters collaboration, and speeds up data science project execution to accelerate the data-to-insights journey.
Concluding Thoughts:
Both Artificial Intelligence (AI) and GenAI have ushered in a new era of technological innovation. While AI excels in data-driven analysis and decision-making, GenAI introduces an imaginative facet to problem-solving. Together, they promise a future where analytical rigor and creative flair coalesce, transforming industries and the way we experience the world. As technology advances, the intertwining of these AI models will play a pivotal role in shaping our digital tomorrow. And data science platforms will be the key enablers for ensuring successful artificial intelligence (AI) adoption in organizations.
You might be interested in
22 Jan, 2026
Why storing everything is not the optimal email archiving strategy for 2026



